knime-shapefiles-as-WKT
Spatial Processing Nodes for KNIME
The “Spatial Processing Nodes” collection of nodes propose to read and write spatial data from various formats, and provide basic transformation, filtering and visualization features.
Alternatives and originality
At some point of time came the question: how to read shapefiles in KNIME? Several other collections of nodes enable the manipulation of spatial data in KNIME:
- The Shapefile extension offers nodes to read ESRI shapefiles (either polygons or polylines). The spatial information (the lines or polygons) are stored in a column having a specific format. This spatial information can then be displayed using the OpenStreetMap nodes.
- The OpenStreetMap nodes enable to filter rows to keep only the geometries within a given geometry and to plot markers upon an openstreetmap background.
- The Palladian Geo Nodes offer to deal with point-based data. They mostly can be used to extract locations based on postal adresses, and display them on a map.
These collections do provide interesting features, but also suffer limitations regarding spatial processing:
- they do not provide reading nor writing in many formats (GML, shapefiles, databases);
- they only support limited data types (points, lines, polygons) whilst in practice all the standard ones are found;
- they store spatial information as a specific data type in KNIME, thus limiting the integration with the other KNIME features; for instance it is difficult for a user to forge a geometry from other data.
We decided to create another collection of nodes which overcomes these limitations:
- the spatial data is stored as a String column in Well-Known Text representation (WKT). This approach permits users to read the geometries in a human-readible format when it flows as tables along computations; this also enables users to forge geometries by themselves if they want.
- we provide numerous nodes to read and write data in many standard formats (see features below)
- we also provide numerous nodes to manipulate geometries by extracting their spatial properties (type, coordinates) and by computing spatial properties (area, distances)
- the computations are delegated to the geotools library, which stands as a reference for spatial processing in Java, and is used in well-known products such as Geoserver.
Limitations
This collection does not intend to turn KNIME into a Geographic Information Systems.
Tools dedicated to this usage will always be better for this “pure” usage.
However if you have to merge data with spatial data, or extract data from spatial data, this might be of use.
Features:
Read spatial data from several formats:
Read information from:
- Spatial databases including postgis
- ESRI shapefile format; we support all the types of geometries, including lines, points or polygons.
- KML
- GML v3
- GeoJSON
- GeoTIFF
Write spatial data into several format
Write spatial data into:
- Spatial databases, including postgis,
- ESRI shapefileformat, with the limitations inherent to this old file format (short column names, limited count of columns, etc.)
- KML
- GML v3
- GeoJSON
Projection and reprojection
Spatial data ultimately corresponds to a pile of (x,y) coordinates. They only have a geographical meaning if they are considered according to a Coordinate Reference System which defines where in Earth these coordinates are. Coordinate Reference Systems might cover the entire planet with limited precision and risks of distortion, or might only cover a limited portion of the globe with high accuracy.
Our collection deals with CRS in every step:
- when reading data, the CRS is detected (when available, as for shapefiles) or infered
- when data flows in KNIME, the CRS is transmitted as a property of the column of the data table (and can thus be viewed there)
- the user can reproject geometries using the “Reproject” node compliant with standard coordinate systems,
- the CRS is written along with the data according to the standard specifications
Properties
Features enable to get the properties of geometries:
- extract 2d coordinates into double columns,
- get the geometry type into a string column,
- extract the coordinates of geometries
Transformation
We provide basic features such as:
- computation of surface (including an automatic transformation to get the surface as squared meters)
- centroid computation,
- versalile nodes to filter rows according to spatial properties, or to compute additional columns, based on the “Extented Contextual Query Language”. Those enable users to write queries based on surface, distance, proximity and other spatial operations.
- nodes to compute relations between two sets of spatial entities (such as detection of overlapping),
- nodes to compute operations between two sets of spatial entities (such as the computation of the union or substraction between entities)
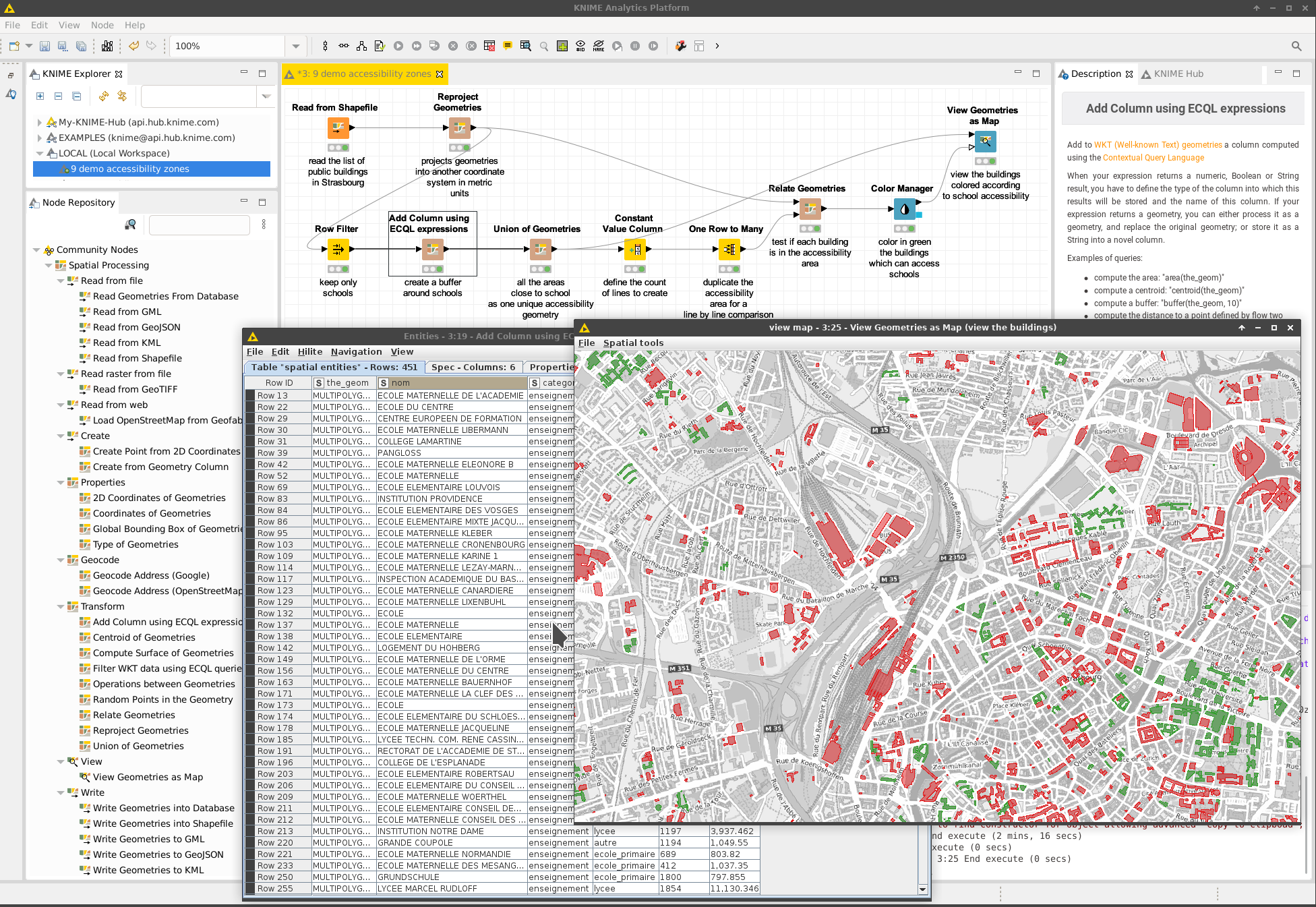
Visualization
Visualisation of spatial data was developed in order to facilitate the verification of the transformations. It is compatible with the standard KNIME coloring of rows done by the Color Manager.
Installation
You can install these nodes in KNIME 4.6 or above following these steps:
- in KNIME, open Help/Install new software
- Click top right button “Add”, and add the repository:
- name: “KNIME EIFER Repository”
- Location: https://knime.res-ear.ch
- After clicking ok, select this “KNIME EIFER Repository” entry in the combo box,
- Select the collection of nodes named “Shapefiles nodes for KNIME based on GeoTools”
- Follow the guidance from KNIME to install
Demo, examples
You can download all the demo workflows here.
- read geometries from ESRI shapefiles
- merge shapefiles in KNIME
- reproject geometries
- write spatial data into a shapefile
- convert KML into shapefile format
- use the color manager to edit symboloty
- compute the surface of geometries
- extract shapefile data to Excel
- extract raster data in GeoTIFF and vectorize it
- compute the accessibility of buildings to services
Copyright and License
Copyright (c) 2022 EIFER (European Institute for Energy Research). This program and the accompanying materials are made available under the terms of the GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE which accompanies this distribution, and is available at https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.html
Source code
The source code is shared in GitHub. Contributions are warmly welcomed. Please report bugs, or feature requests, in the GitHub bugtracker